Design of Aging Test System for SiC MOSFET Modules
ID:60
Submission ID:23 View Protection:PUBLIC
Updated Time:2021-08-20 19:33:56
Hits:1204
Poster Presentation
Start Time:2021-08-27 12:08 (Asia/Shanghai)
Duration:1min
Session:[P] Poster » [P1] Poster 1
Abstract
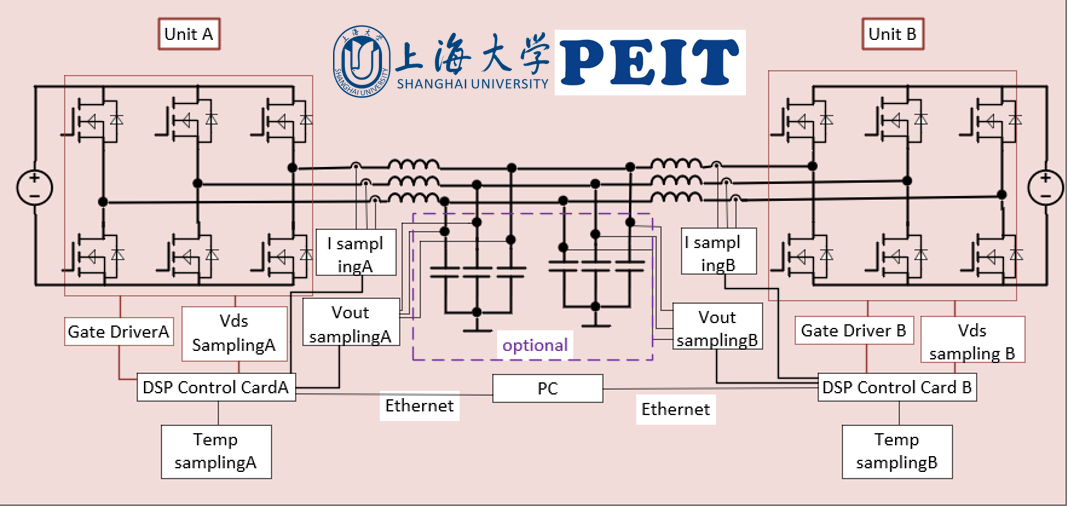
Silicon carbide (SiC) materials are well known for their high speed, high temperature and high power characteristics. Converters using SiC devices can greatly reduce the volume of magnetic components and radiator, as well as reduce the cost of converters, which is getting more widespread. While the technology is getting more mature, the reliability of SiC power devices still remain a top concern, which is mainly caused by the aging problem of devices. The aging problem can eventually result in the damage of device itself and converters, so it is significant to do aging researches. An aging test bench which can emulate practical working conditions of converters and real stress of devices, then establish the relationship between the working conditions and the reliability indexes, will be a significant contribution to the reliability research of both device and converter. To design an aging test system for power devices, it is necessary to propose an accelerated method which generates thermal cycling impacts on the devices, so as to effectively monitor the aging characterization of power devices. Furthermore, the aging test system should meet the requirements of emulating real working conditions and low power loss, simultaneously. However, this type of aging test systems is mainly designed for IGBT modules so far, and not directly applicable for SiC modules. Therefore, this paper proposes a new power cycling aging test system for SiC modules, facilitating the investigation on the aging of SiC modules.
Keywords
Reliability,Aging Test System,Power Cycling,SiC Module






Comment submit